Graphite molds are the most widely used basic process equipment in industrial production, and the mold industry is the basic industry of the national economy. In modern industrial production, stamping, forging, die-casting, extrusion, plastic injection or other forming processing methods are widely used for product parts, which are matched with forming dies to form blanks into parts that meet product requirements. All kinds of tools and products we use in our daily production and life, from the base of the machine tool, the shell of the machine body, to the shell of a screw, button and various household appliances, all have a close relationship with the mold. The shape of the mold determines the shape of these products, and the processing quality and precision of the mold also determine the quality of these products. In recent years, the mold industry has developed rapidly. Graphite materials, new processes and increasing mold factories continue to impact the mold market. Graphite has gradually become the material for mold making with its good physical and chemical properties.
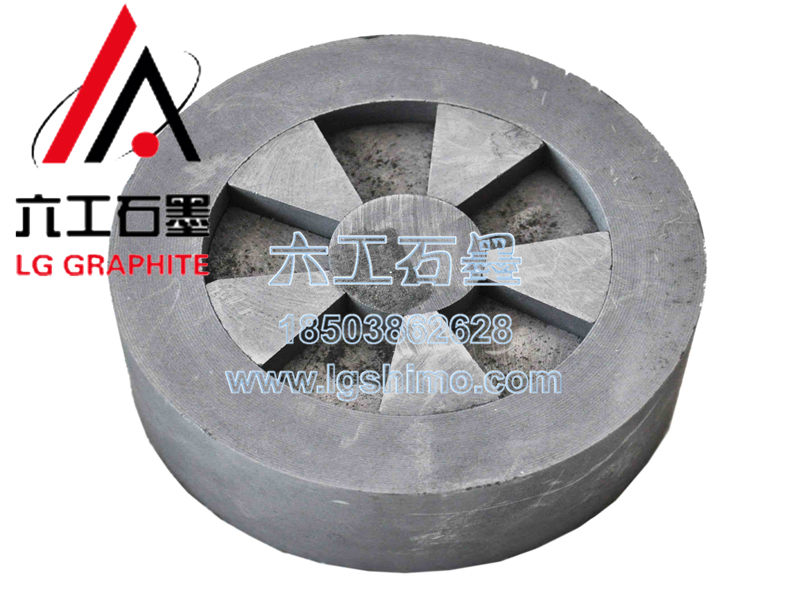

At present, graphite molds have been widely used in the following aspects:
- Graphite molds for continuous casting and semi-continuous casting of non-ferrous metals:
In recent years, advanced production methods such as direct continuous (or semi-continuous) production of bars or tubes from molten metal state are being promoted at home and abroad. This method has been adopted in China in copper, copper alloy, aluminum, aluminum alloy and so on. - Mold for pressure casting:
Artificial graphite materials have been successfully used for pressure casting of non-ferrous metals. For example, zinc alloy and copper alloy castings produced by pressure casting molds made of artificial graphite materials have been used in automotive parts and the like. - Graphite mold for centrifugal casting:
Graphite molds have been successfully used in centrifugal casting. In order to prevent the burning of artificial graphite molds, anti-oxidation measures can be taken. After casting a number of castings, if the inner surface of the mold is found to be burnt, the size of the inner hole of the mold can be enlarged to be used to cast large-sized casing.